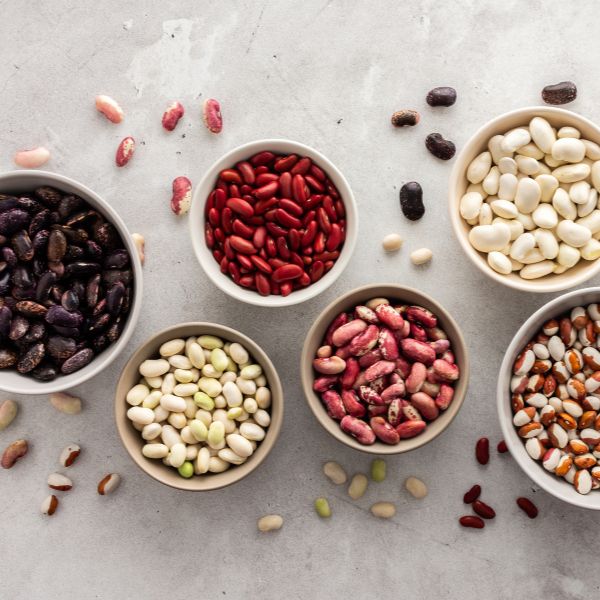
Much of the conversation around plant-based foods involves replicating the texture and taste of popular meats like chicken and beef. Yet the variety of existing plant-based protein sources get sidelined, including beans!
Much of the conversation around plant-based foods involves replicating the texture and taste of popular meats like chicken and beef. Yet the variety of existing plant-based protein sources get sidelined, including beans!
While not a complete protein, beans provide a high amount per serving and are also a good source of fiber, vitamins, phytochemicals and other nutrients. Learn more about what beans can add to your diet.
Protein Content
The amino acid content in protein helps the tissues in your body repair themselves, from muscles to skin and hair. Complete proteins contain 20 amino acids, including all nine essential types.
Excluding soybeans, the typical bean offers all nine essential amino acids but not the full 20. Those seeking to consume complete proteins are advised to combine beans with dairy products or nuts, seeds, corn or grains for vegans.
Even on their own as an incomplete protein, beans:
- Offer a low-fat, low-calorie source of protein enriched with fiber. A cup-size serving of beans offers 15 grams of protein.
- Help you feel fuller with fewer calories, aiding long-term weight loss and reduced consumption of saturated fat.
Nutritional Profile
In addition to protein, beans are full of various vitamins, minerals and other nutrients. They provide a source of:
- Dietary Fiber: Benefits include lower risks for heart disease, certain cancers, high blood pressure and high cholesterol. A one-cup serving offers just under 20 grams of fiber.
- Folate: An essential nutrient for generating red blood cells and reducing neural tube defects during pregnancy.
- Iron: Helps your body create the proteins present in your blood, supports its connective tissue and can help regulate hormones.
- Magnesium: Helps your body generate proteins, bone tissue and is essential for controlling blood sugar spikes.
- Potassium: An essential nutrient for kidney, muscle and nervous system health.
- Zinc: A mineral that helps strengthen your immune system, control inflammation and improve wound healing.
- Antioxidants: Support your body by fighting free radicals and reducing oxidative stress and cellular damage.
Health Benefits
Considering the nutrients found in a single cup of beans, this plant-based protein is associated with a number of health benefits, including:
- Heart Health: Eating more beans can help your body fight against certain conditions that contribute to cardiovascular issues, like LDL or “bad” cholesterol and high blood pressure. These factors then help lower your risks for heart disease, a stroke or heart attack.
- Diabetes: Regularly consuming beans can help manage blood sugar spikes, glucose levels and control cravings. Studies have found that people who regularly consume beans tend to have lower risks for developing type 2 diabetes.
- Gut Health: A balanced microbiome often means a stronger intestinal barrier and healthier immune system. Beans deliver these benefits through their high fiber content.
Multiple Preparation Options
Part of the legume family, beans cover a broad spectrum from black, pinto and red beans to chickpeas, navy beans, black-eyed peas and soybeans. They can either be packaged dry and need to be rehydrated before cooking or come ready to add to your recipe from the canned or frozen foods section at the store.
For some inspiration on how to use beans:
- Give your salad or soup more protein by adding a cup of prepared beans.
- Create a dip like hummus to have with raw vegetables.
- Take a plant-based approach to Mexican and Tex-Mex recipes by replacing ground beef, pork or chicken with beans.
- Explore recipes including beans from across the world to get familiar with various flavors, textures and preparation methods.
Discover what’s possible with beans at Colony Diner on our regular menu and vegan menu!