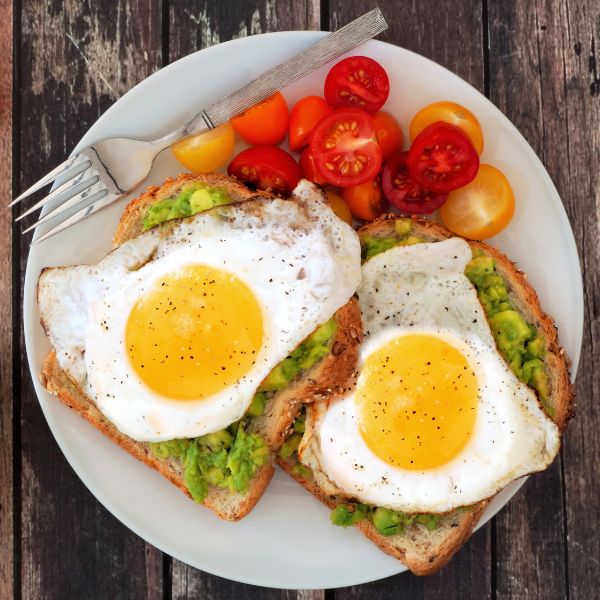
When you make the decision to eat healthier, dietary changes often start with consuming more greens, fiber and antioxidants, while cutting down on harmful fats and cholesterol. For breakfast, baking and other meals, using egg whites also seems like a logical choice.
When you make the decision to eat healthier, dietary changes often start with consuming more greens, fiber and antioxidants, while cutting down on harmful fats and cholesterol. For breakfast, baking and other meals, using egg whites also seems like a logical choice.
Yet egg yolks have multiple nutritional benefits too! The decades-old assumption that they directly fuel high cholesterol has since been partially debunked.
As you make choices about what to eat, learn about the differences between egg yolks and egg whites.
Overall Benefits of Eggs
In their whole form, eggs offer more protein per serving than dairy and meat. The yolk provides the greatest concentration, over 16 grams versus 10 grams for the white per 100-gram serving.
In terms of your health and monitoring calories in conjunction with protein, the typical egg comes to about 70 calories. The high amount of protein per serving helps you feel fuller and more satisfied.
Benefits of the Yolk
The composition of a yolk is split evenly between a moisture and solid, which itself includes protein, fats and emulsifiers. As a result, the yolk is the egg’s primary source of cholesterol but also has a different nutritional composition than egg whites.
Today, fats don’t have the same reputation as decades ago. In thinking about your diet, eggs provide a source of healthy fats, attributed to the yolk’s higher monounsaturated content and polyunsaturated fats like omega-3 fatty acids. However, the yolk does contain a small amount of saturated fat, which accounts for under 10 percent of your recommended intake.
The egg yolk is also a rich source of nutrients, including vitamins A, E, D and K, as well as vitamins B2, B12, B5, B6 and folate. You’ll also obtain traces of calcium, iron, zinc, copper, phosphorous, selenium and manganese.
To be mindful of cholesterol, aim for no more than 300 milligrams per day, including from whole eggs and other sources, to maintain optimal heart health.
What About Egg Whites?
Strictly consuming egg whites became more popular a couple of decades ago in response to low-fat diets and concerns about dietary cholesterol elevating HDL and LDL levels. Since then, research has shown that consuming sources of dietary cholesterol doesn’t immediately impact LDL and HDL levels, especially in conjunction with a healthy, varied diet and moderate exercise.
The albumen or egg whites by themselves are low in both calories and fats, while offering a moderate source of protein. In turn, egg whites are ideal for those looking to get more protein without a source of fat and those following a low-calorie diet.
In evaluating what you eat, egg whites are also considered a complete source of protein, delivering all nine essential amino acids. While egg yolks help you feel full, egg whites are an ideal protein replacement for weight loss, including for meat, fish and dairy.
While they are not as nutrient-dense as the yolk, egg whites provide a source of B vitamins, as well as minerals like iodine, selenium and phosphorus.
Explore all the ways that eggs can be used for breakfast, lunch and dinner at Colony Diner! Browse our menu before stopping in for a meal or placing an order for takeout.